Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a widespread oral health issue affecting millions of people worldwide. Understanding the prevalence of gum inflammation is crucial as it underscores the significance of addressing this condition to maintain overall oral health. Beyond its prevalence, grasping the impact of periodontal infection on oral health is paramount. Untreated gingivitis can lead to serious complications, including tooth loss, bone damage, and systemic health problems. In this blog, we’ll learn about what is gum disease and the prevalence and impact of gum disease is essential for individuals to prioritize preventive measures and seek timely treatment to preserve their oral health and overall well-being.
What is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, also called periodontal disease, starts when plaque builds up on teeth. If not removed by brushing and flossing, it can cause gum inflammation (gingivitis). If untreated, gingivitis can become periodontitis, spreading deeper into the gums and potentially damaging the bone that supports the teeth. Signs of gingivitis include swollen or bleeding gums, bad breath, and loose teeth. To prevent and treat gingivitis, it’s important to practice good oral hygiene and see your dentist regularly.
Different Stages of Periodontal Infection
Periodontal infection progresses through two main stages: gingivitis and periodontitis. Understanding the characteristics and implications of each stage is crucial for effective prevention and treatment.
Gingivitis
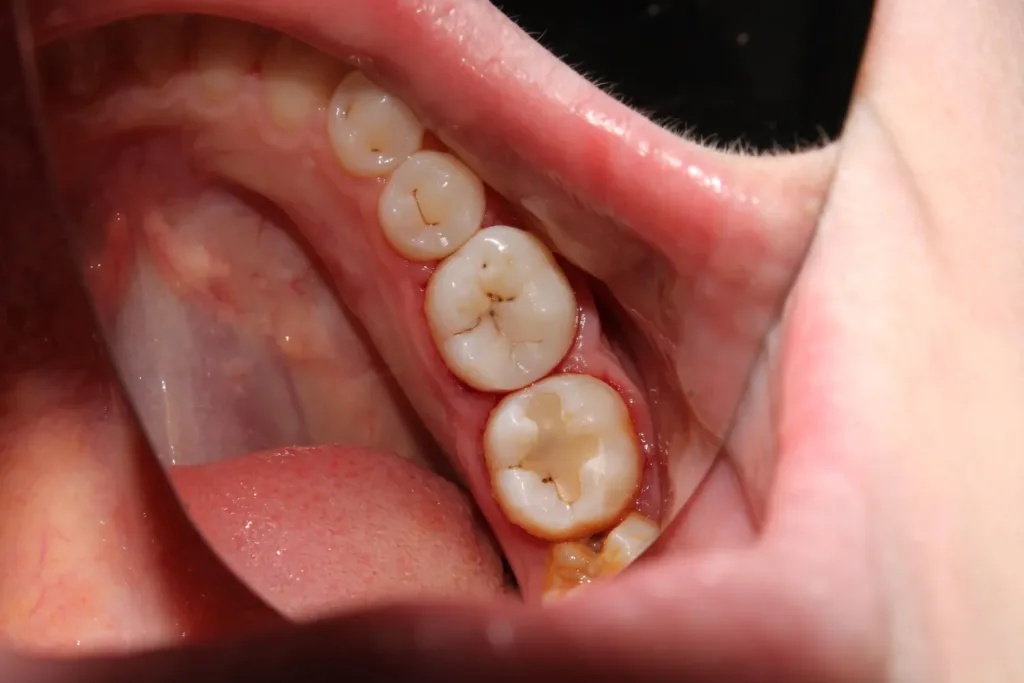
Gingivitis is the first stage of inflammation and happens when gums become inflamed. Plaque, a sticky bacteria film, builds up on gums due to not brushing or flossing well. Plaque produces toxins that irritate the gums, causing them to become red, swollen, and prone to bleeding, particularly during brushing or flossing. While gingivitis is reversible with proper oral care, untreated gingivitis can progress to a more severe form of inflammation known as periodontitis.
Periodontitis
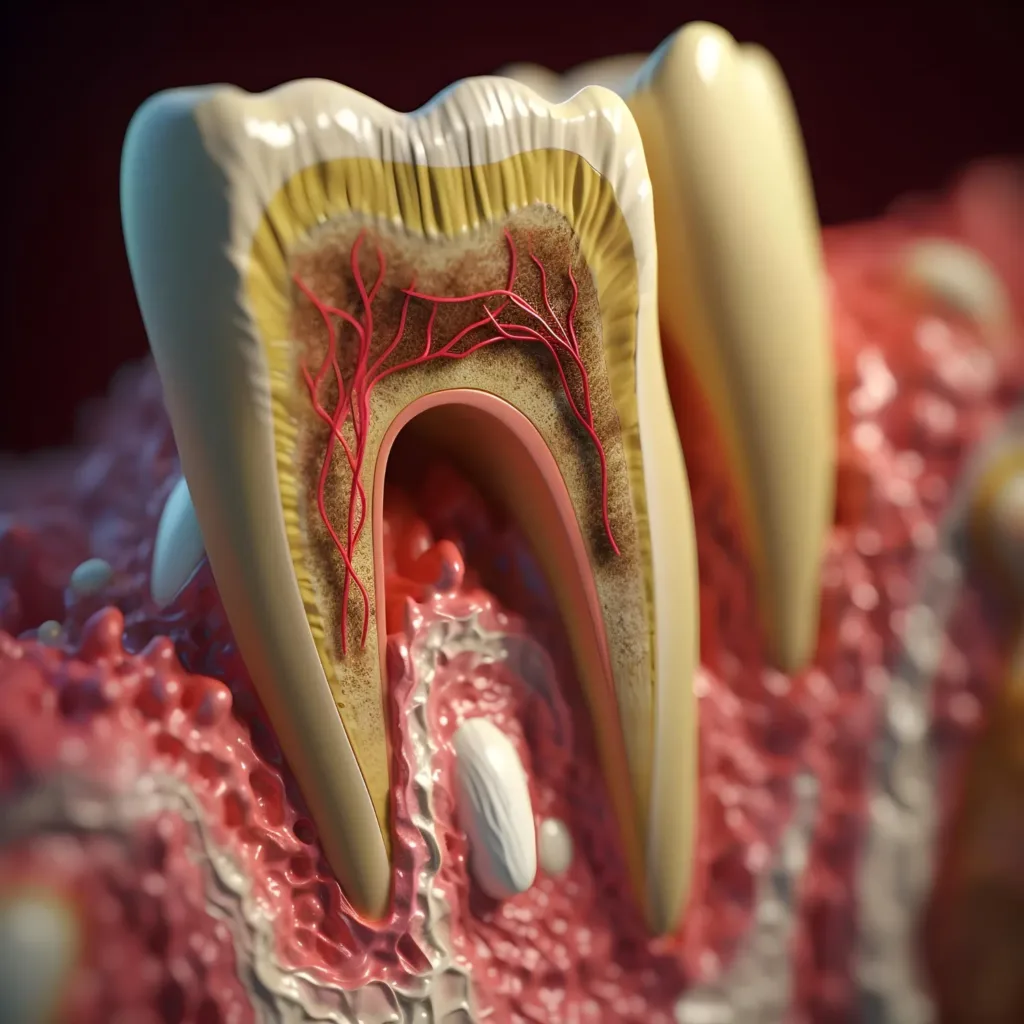
Periodontitis is an advanced stage of periodontal infection characterized by the destruction of the tissues and bones that support the teeth. Plaque turns into tartar under the gumline, letting bacteria grow and produce toxins. This causes inflammation, which damages gum tissue and bone. Signs of periodontitis include receding gums, deep pockets between teeth and gums, bad breath, and loose teeth. Without treatment, it can lead to tooth loss and affect overall health.
Factors Contributing to the Development of Gum Disease
Several factors can contribute to the development and progression of gum disease. Understanding these factors is essential for preventing and managing the condition effectively.
Poor Oral Hygiene Practices
Not brushing and flossing enough lets bacteria build up on teeth and gums, causing gum inflammation. This buildup turns into tartar, which makes gums inflamed and can lead to gum inflammation if not treated.
Tobacco Use
Smoking and tobacco use are significant risk factors for inflammation. Tobacco products harm gums by reducing blood flow, weakening the immune system, and slowing healing. This puts smokers at higher risk for inflammation and more severe symptoms than non-smokers.
Genetics
Genetics also play a role in the development of gum disease. Some people are born with gums that are more prone to problems or react strongly to plaque. Even though we can’t change our genes, knowing about these tendencies can encourage us to take better care of our teeth and gums and see the dentist more often.
Health Conditions
Certain health conditions can increase the risk of periodontal infection. Conditions such as diabetes, immune system disorders, and hormonal changes (such as during pregnancy or menopause) can impact gum health and make individuals more susceptible to periodontal infection. Managing these underlying health conditions and maintaining optimal oral hygiene is crucial for reducing the risk of gum inflammation.
Medications
Certain medications can harm oral health and lead to inflammation. Drugs that cause dry mouth or change saliva production can make it easier for bacteria to grow and plaque to build up. People on these medications need to be extra careful with brushing and flossing and might need to see their dentist more often to check their gums.
Signs and Symptoms
Knowing the signs of inflammation early is important to stop it from getting worse and causing problems. Recognizing these signs helps people get dental help quickly and take steps to keep their mouths healthy.
Swollen, Red, or Tender Gums
One of the early signs of periodontal infection is gum inflammation, characterized by swollen, red, or tender gums. Healthy gums should appear pink and firm. However, when affected by gum disease, the gums may become swollen and inflamed, indicating an underlying issue.
Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums, particularly during brushing or flossing, are a common symptom of inflammation, especially in its early stage known as gingivitis. Bleeding occurs due to the irritation and inflammation of the gum tissue caused by plaque buildup along the gumline.
Persistent Bad Breath
Chronic bad breath, also known as halitosis, can be a sign of inflammation. The presence of bacteria in the mouth, resulting from plaque and tartar buildup, can produce foul-smelling odors. Despite practicing regular oral hygiene, persistent bad breath may indicate an underlying gum infection requiring professional dental care.
Receding Gums
As periodontal infection progresses, the gums may begin to recede or pull away from the teeth, exposing the tooth roots. Gum recession not only affects the aesthetics of the smile but also increases the risk of tooth decay and sensitivity.
Deep Pockets Between Teeth and Gums
Healthy gums fit snugly around the teeth, forming shallow gum pockets. In contrast, periodontal infection can cause these pockets to deepen, creating spaces where bacteria thrive and further damage the surrounding tissues and bone.
Loose or Shifting Teeth
In advanced stages of periodontal infection, such as periodontitis, the supporting bone and tissues that hold the teeth in place may deteriorate, leading to tooth mobility or shifting. Loose teeth are a concerning symptom of severe inflammation and may indicate the need for immediate dental intervention.
Prevention and Treatment
Effective prevention and treatment strategies are vital in maintaining healthy gums and teeth. Below are key approaches to preventing and treating inflammation:
Prevention Methods
Prevention of gum inflammation involves consistent oral hygiene practices, including brushing teeth with fluoride toothpaste twice daily and daily flossing to remove plaque and bacteria. A healthy diet, rich in fruits and vegetables and low in sugary snacks, supports gum health. Additionally, avoiding tobacco products is crucial as smoking increases the risk of gum inflammation. These preventive measures help to maintain optimal oral hygiene and reduce the likelihood of developing gingivitis or periodontitis.
Professional Dental Care
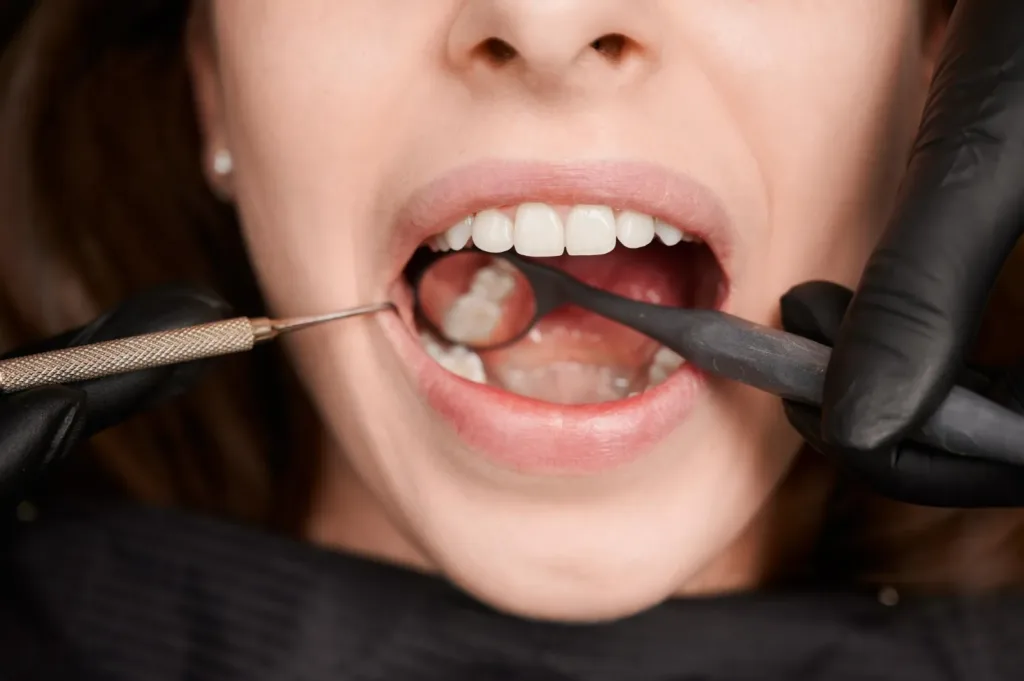
Going to the dentist regularly is important for keeping your mouth healthy. Dentists check for problems like gum diseases, cavities, and oral cancer. They clean your teeth to remove plaque and tartar, which can cause periodontal infections. Dentists also give you tips on how to take care of your teeth at home. They might suggest treatments like fluoride or sealants to prevent problems. Seeing the dentist regularly helps you keep your mouth in good shape and stops dental issues from getting worse.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for periodontal infections include two types: non-surgical and surgical. Non-surgical treatments, like scaling and root planing, work well for mild cases like gingivitis. But for severe periodontitis, surgeries like flap surgery or bone grafts might be needed to fix gums and stop more harm. Also, medicines such as antibiotics or mouth rinses can control bacteria. These treatments aim to clean bacteria, plaque, and tartar, decrease swelling, and help gums heal, all to keep the mouth healthy.
Conclusion
Taking care of your gums is very important for keeping your mouth healthy. These can make your teeth hurt and increase the chances of losing them. They can also lead to other serious health problems like heart disease or diabetes. Additionally, if your gums are unhealthy, it can affect how confident you feel and your quality of life because of bad breath or how your smile looks. That’s why you should make sure to brush and floss your teeth well, go to the dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings, and get treatment quickly if you notice any signs of gum disease. You can make an appointment in Brooklin Dental Centre to schedule a dental check-up and keep your gums healthy and your smile bright. Taking care of your gums now can help you avoid dental problems later and make you feel better overall.